Enforcing company-wide cost-saving policies around printing, travel, etc. further helps minimize overhead. This comprehensive guide breaks down overhead rate calculation into clear, actionable steps any business can follow. Let’s say we want to calculate the overhead cost of a homemade candle ecommerce business. Then, they’ll need to estimate the amount of activity or work that will be performed in that same time period. For this example, we’ll say the marketing agency estimates that it will work 2,500 hours in the upcoming year. Conversely, the cost of the t-shirts themselves would not be considered overhead because it’s directly linked to your product (and obviously changes based on the volume of products you create and sell).
D. Apply Overheads During Production
Indirect costs are those that cannot be easily traced back to a specific product or service. For example, the office rent Catch Up Bookkeeping mentioned earlier can’t be directly linked to any one good or service produced by the business. The differences between the actual overhead and the estimated predetermined overhead are set and adjusted at every year-end.

Accounting for Startups The Ultimate Startup Accounting Guide

Predetermined overhead rate is the estimated overhead that will allocate to each product at the begining of accounting period. It is equal to the estimate overhead divided by the estimate production quantity. First, you need to figure out which overhead costs are involved, and then create a total of this amount.
Setting pricing
The predetermined overhead rate is calculated by dividing the estimated manufacturing overhead by the estimated activity base (direct labor hours, direct labor dollars, or machine hours). For instance, if the activity base is machine hours, you calculate predetermined overhead rate by dividing the overhead costs by the estimated number of machine hours. This is calculated at the start of the accounting period and applied to production to facilitate determining a standard cost for a product. This activity base is often direct labor hours, direct labor costs, or machine normal balance hours.
For example, if you add a new production facility, experience dramatic changes in utility costs, or significantly change your production methods, it makes sense to revisit your overhead rate. In this guide, we’ll walk through a step-by-step process for calculating the predetermined overhead rate, its importance, and best practices for accuracy. Hence, you can apply this predetermined overhead rate of 66.47 to the pricing of the new product X. There are several reasons why businesses need to calculate a predetermined overhead rate. Company X and Company Y are competing to acquire a massive order as that will make them much recognized in the market, and also, the project is lucrative for both of them. After going to its terms and conditions of the bidding, it stated the bid would be based on the overhead rate percentage.
- Direct costs are costs directly tied to a product or service that a company produces.
- That is, a number of possible allocation bases such as direct labor hours, direct labor dollars, or machine hours can be used for the denominator of the predetermined overhead rate equation.
- This project is going to be lucrative for both companies but after going over the terms and conditions of the bidding, it is stated that the bid would be based on the overhead rate.
- Now management can estimate how much overhead will be required for upcoming work or even competitive bids.
- The adjustment made to eliminate this difference at the end of the period is called the disposition of over or underapplied overhead.
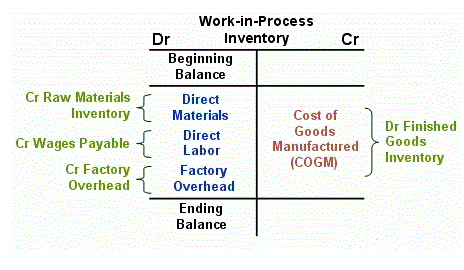
Take, for instance, a manufacturing company that produces gadgets; the production process of the gadgets would require raw material inputs and direct labor. These two factors would definitely make up part of the cost of producing each gadget. The company, having calculated its overhead costs as $20 per labor hour, now has a baseline cost-per-hour figure that it can use to appropriately charge its customers for labor and earn a profit. That is, the company is now aware that a 5-hour job, for instance, will have an estimated overhead cost of $100. Applying our formula, we get $188,000 in fixed overhead divided by the base of $376,000 total direct labor dollars for an allocation rate of $0.50 per machine hour. Additionally, predetermined overhead rate the choice of allocation base can significantly impact the calculated rate and, consequently, the overhead cost per unit.
- For most small to medium businesses, categorizing overhead into 5-10 major categories (rent, utilities, indirect labor, etc.) is sufficient.
- Take, for instance, a manufacturing company that produces gadgets; the production process of the gadgets would require raw material inputs and direct labor.
- Challenges include the potential for distortion if estimated overhead costs or allocation bases are inaccurate.
- The equation for the overhead rate is overhead (or indirect) costs divided by direct costs or whatever you’re measuring.
- As explained previously, the overhead is allocated to the individual jobs at the predetermined overhead rate of $2.50 per direct labor dollar when the jobs are complete.
This means that if an actual overhead rate is used by the business, the costs of products manufactured in summer will be higher than cost of goods manufactured in the winter. To tackle this problem predetermined overhead rates are used instead of actual overhead rates. As stated above, it involves calculating the total manufacturing overhead cost and dividing it by an activity base. Based on this definition, the formula for the predetermined overhead rate is below. The estimated overhead costs represent the total anticipated indirect expenses for a specific period.
The Predetermined Overhead Rate Formula
- The management concern about how to find a predetermined overhead rate for costing.
- Manufacturing overhead costs include all manufacturing costs except for direct materials and direct labor.
- For every hour a line worker records directly creating a purse, we allocate $10 in fixed overhead to that item.
- The period selected tends to be one year, and you can use direct labor costs, hours, machine hours or prime cost as the allocation base.
- However, if there is a difference in the total overheads absorbed in the cost card, the difference is accounted for in the financial statement.
Detailed cost analysis helps to estimate the cost of overheads with accuracy. Further, customized input from different departments can be obtained to enhance the accuracy of the budget. Once costs are broken down, small businesses can assess if any categories are excessive. For example, upgrading to energy-efficient equipment could reduce utilities. Renegotiating contracts with vendors may yield savings on supplies or services.
Examples of Overhead Rates
But determining the exact overhead costs is not easy, as the cost of electricity needed to dry, crush, and roast the nuts changes depending on the moisture content of the nuts upon arrival. Yes, it’s a good idea to have predetermined overhead rates for each area of your business. Now, let’s look at some hypothetical business models to see actual use-cases for predetermined overhead rates. Various tools help in calculating and applying predetermined overhead rates effectively.


